Cellular Respiration vs. Photosynthesis
Breathing. It is what all animals and plants must do to stay alive.
Wait, did you say plants?
Yes, I did?
How can plants breathe if they do not have lungs or gills?
Many animal species do not have lungs or gills and breath through their skin, such as Earthworm Jim.
OK, but earthworms are animals. What about plants?
Plants have little pores on the underside of their leaves called stomata. Carbon dioxide enters the plant through the stomata, and most of the oxygen produced during photosynthesis leaves through the stomata.
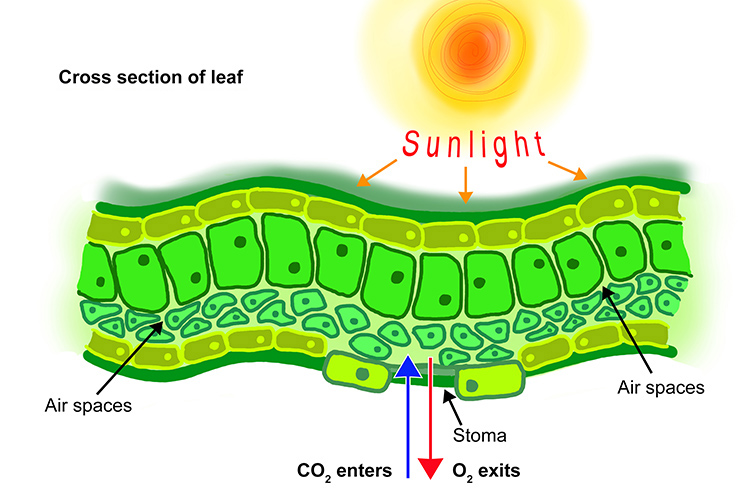
Water also leaves through the stomata, a process called transpiration.
Ok. Thanks to your epic chapter on photosynthesis, I know why plants need CO2, but why do they need oxygen?
Good question. To answer it, I need to introduce you to cellular respiration.
Photosynthesis occurs in the chloroplasts in plants and algal cells. During photosynthesis, light energy, water, and CO2 convert to oxygen gas (O2) and glucose (C6H12O6). Plants then glue a bunch of glucose molecules together to make a large storage molecule called starch.
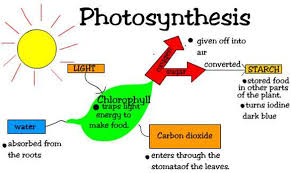
Why do they store it as starch?
Good question. Starch is a very stable molecule that can store a lot of energy. However, plants need the energy to grow and do plant-related activities. Plants cannot directly access the energy in starch, so they break it down into glucose.
So they use glucose as a direct energy source?
No. Plant cells require the highly reactive molecule ATP to do everything that plants do. So, plant cells use cellular respiration to convert the energy in glucose into ATP.

Here is the chemical formula for photosynthesis:
6 CO2 + 6 H2O + light energy —> 6 O2 + C6H12O6 (glucose)
Here is the chemical formula for cellular respiration:
6 O2 + C6H12O6 (glucose) —> 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + energy (ATP and Heat)
How are the two formulas similar?
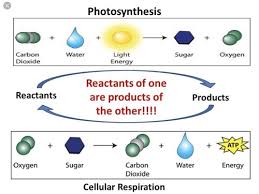
Well, both formulas have the same molecules – i.e., glucose, oxygen, water, and CO2.
Good. And how are the processes different?
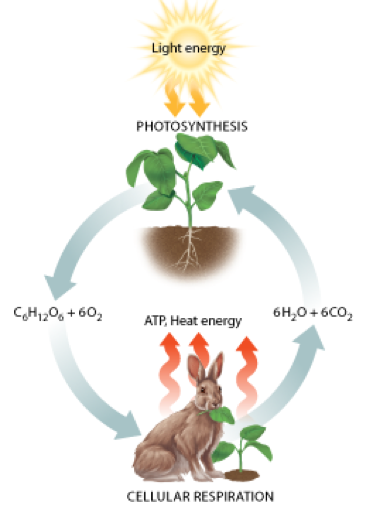
Photosynthesis is a process that stores energy in glucose, and cellular respiration releases the energy in glucose. Also, the reactants in photosynthesis are the products of cellular respiration. And the products of photosynthesis are the reactants of cellular respiration.
Awesome possum. Here is everything you explained in two nice pretty pictures.
I like the pictures.
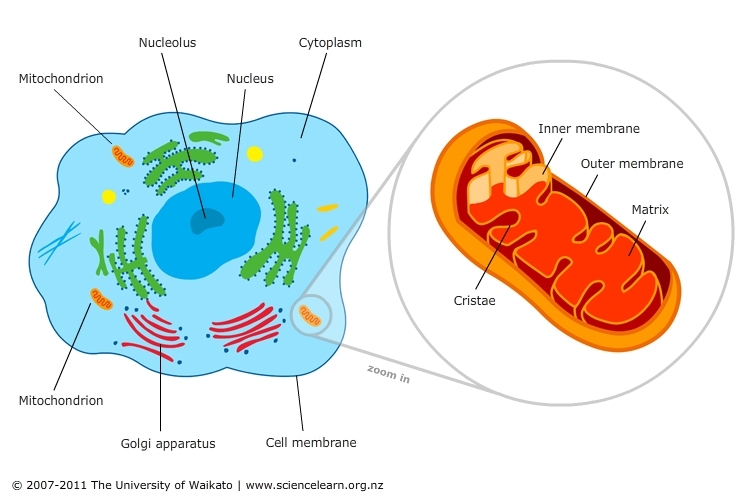
The Mitochondria (aka The Powerhouse of the Cell, aka Sally)
Plant cells and animal cells have mitochondria. Mitochondria – THE POWERHOUSE OF THE CELL!!!!!!! – make most of a cell’s ATP. However, mitochondria can only make ATP in the presence of oxygen via cellular respiration.
Cellular Respiration (aerobic respiration)
Cellular respiration is an aerobic process, which means it requires oxygen. However, the first step in cellular respiration is anaerobic because it does not need oxygen.
There are three stages to cellular respiration:
- Glycolysis
- Kreb’s cycle
- Electron transport chain
Glycolysis
Glycolysis is an anaerobic process that occurs in the cytoplasm of a cell. The cytoplasm is the liquid inside of a cell. Glycolysis means to split (lysis) sugar (glyco). Here is how it works:
- The cell uses two ATPs’ energy to split glucose into two three-carbon molecules called pyruvic acid (pyruvate).
- The splitting of glucose releases electrons, which are picked up by the energy taxi NAD+. When NAD+ gains electrons, it becomes NADH, taking the electrons to the electron transport chain.
- Glycolysis produces four ATPs for a net gain of 2 ATPs. (The cell had to use two ATPs to start the process; therefore, 4 ATPs – 2 ATPs = 2 ATPs.)

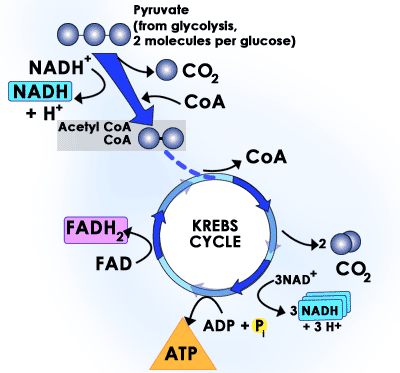
The Krebs Cycle (aka The Citric Acid Cycle)
The two pyruvic acid molecules move to the mitochondria but can only enter if oxygen is present. In the presence of oxygen, the pyruvic acid molecules convert to citric acid, which releases some energy as ATPs and heat. Electrons are shed in the process, which the energy taxies NADH and FADH2 pick up. Also, the conversion of pyruvic acid to citric acid releases CO2, and this is where the CO2 we exhale comes from.
The Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
The electron transport chain is an aerobic process that produces the majority of a cell’s ATPs. Here is how it works:
- The electron taxies NADH and FADH2 release their energy into the ETC.
- The movement of the electrons pumps a bunch of H+ ions toward ATP synthase.
- The H+ ions diffuse (move) through ATP synthase, converting ADP + P into ATP.
- Oxygen and hydrogen ions collect the electrons at the ETC’s end, forming H2O.
/electron-transport-chain-58e3be435f9b58ef7ed96112.jpg)
Summary
So plant cells use both CO2 and O2, and animal cells only use O2. Plants use CO2 to make glucose during photosynthesis, and plants and animals use O2 to break glucose down into ATP.