Let’s review what you have learned about evolution:
- Mutations are random events that create a new allele.
- Natural selection is a nonrandom process that favors traits with higher fitness. Organisms with higher fitness are more likely to survive and reproduce and pass on their traits to their offspring. Therefore, the trait (phenotype) allele frequency with higher fitness will increase, and the allele frequency of the traits with a lower fitness will decrease.
- Gene flow is the migration of individuals into and out of populations.
- In genetic drift, no phenotype (trait) has an adaptive advantage (fitness) because an organism’s survival is by chance. Therefore, the change of allele frequencies results from who survives the random event ( i.e., volcanic explosion).
What is a species?
A species is a population of organisms that can reproduce fertile offspring (their kids can have kids). However, not all species fit this definition. For example, grizzly bears and polar bears can mate and produce fertile offspring. Polar bear’s and grizzly bear’s territories did not overlap because of their traits. Polar bears are great swimmers, have thicker coats, and their paws act as snowshoes, which help them survive the arctic environment. Grizzlies have thinner coats, sink in deep snow, and are not great swimmers, so they are not well adapted to the arctic tundra. However, as the climate warms, the Arctic has become more hospitable for grizzly bears. Grizzly bears are now entering the warmer arctic tundra, and mating between the two species is occurring. The offspring of the bears are hybrids and are usually fertile.
So, are grizzly bears and polar bears two different species?
Yes.
Why?
Even though the mating bears can make fertile offspring, this is still an uncommon occurrence. Humans define what a species is; therefore, not every organism fits into the definition.

I’m still confused.
Alright. Below is a picture of some basic 2-D shapes.

What shape is this?


Yes. I’m trying to explain something here, so please play along.
Fine. It’s a circle.
Good job.

What shape is this?

A diamond.
Awesome possum!!!!!
Now what shape is this?

It’s a. . . well. . . it is made of many shapes.
True. But, you can only pick one basic 2-D shape.
I don’t even know what that thing is. Is it a dragon?
It’s a dramoose, a dragon-moose hybrid.
Did you spend time drawing that?
No, I found it on the Internet.
Wait?!! There are more people out there that think of these stupid things.
Yes, we’re a population.

Now, pick one basic 2-D shape that best describes the dramoose.
I can’t.
And that is my point. Not everything fits the definition of a term. Therefore, science defines a species based on the criteria that fit most species.
I think I got it. So, are donkeys and horses the same species?
Now a donkey and horse can mate, producing a mule. But, the mule is infertile, so a horse and donkey are separate species.

So, have I confused you?

Point taken.
To simplify, we will stick with the horse and donkey example – i.e., if two organisms mate and cannot produce fertile offspring, they are two separate species. If two species cannot produce fertile offspring, then they are reproductively isolated.
Reproductive Isolation
Reproductive isolation happens when the difference in allele frequencies is great enough to prevent two species from making fertile offspring. Therefore, there is reproductive isolation between the horse and the donkey.
However, the separation of the two populations does NOT mean that speciation WILL happen. If the change in allele frequencies does not lead to reproductive isolation, then there is no speciation. For example, for at least 10,000 years, the people living in the Western world were separated by the Pacific and Atlantic oceans from the people living in the Eastern world. However, when the Europeans came to the Americas, the Native Americans and Europeans could mate and produce fertile offspring. Therefore, there was no speciation.
Type of Reproductive Isolation
- Mechanical Isolation – This happens when the male and female parts are incompatible for mating.

- Gametic Isolation – This happens when the sperm cannot fertilize the egg.

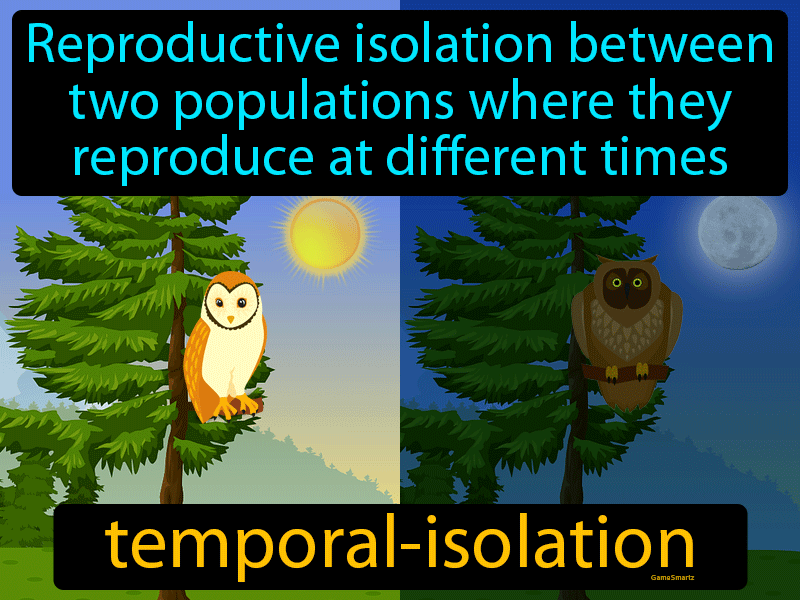
- Temporal Isolation – This happens when species mate at different times of the day, month, or year.
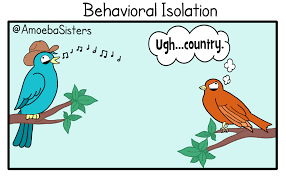
- Behavioral Isolation – This happens when one population will not mate with the other population because they do the other population’s behaviors.
Types of Speciation
Sympatric Speciation
Sympatric speciation occurs when two populations evolve into separate species in the same geographical location. For example, one population lives in the trees and the other on the ground.

Allopatric Speciation
Allopatric speciation occurs when a geographical barrier – i.e., a river or a mountain range – separates the two populations.
![PDF] Peripatric speciation | Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/3d4a47486505f4a6849dfd0a160f06a596ef9791/2-Figure1-1.png)
How Does Speciation Happen?
- A population of the same species splits into two separate populations (allopatric or sympatric).
- The populations face different selection pressures (one species lives in a forest and the other in a meadow).
- Over time, natural selection happens, and the allele frequencies between the two species change.
- The two species come in contact in the distant future but are now reproductively isolated.
- Speciation has happened.

