Rules for Cell Homeostasis
The cells of your body follow some basic rules to maintain homeostasis. These rules are:
- Cells will stop dividing when they come in contact with each other, which prevents the formation of a tumor.
- Most cells can only do cell division if they are attached to a membrane or other cells (blood cells are the exception to this rule).
- Cells follow the rules of cell division.
- Cells will commit apoptosis (self-destruction) at the end of their lifespan or when damaged beyond repair.
When cells follow the above rules, our bodies grow and repair themselves in a controlled manner. However, if a cell breaks the rules, they go rogue and become cancerous.
What is Cancer?
Cancer is uncontrolled cell growth. Most forms of cancer begin spontaneously. A mutation results in the DNA during interphase (usually during DNA replication), and a cell becomes cancerous. When a cell has damaged DNA, the self-destruction genes are activated, and the cell commits apoptosis (controlled cell death). However, sometimes, the self-destruct genes are damaged or do not activate, leading to cancer. Most of the time, specialized white blood cells called T cells recognize and kill the cancerous cell. But cancer is diabolical and can have higher fitness than our healthy cells. When cancerous cells have an adaptive advantage over healthy cells, a tumor develops.
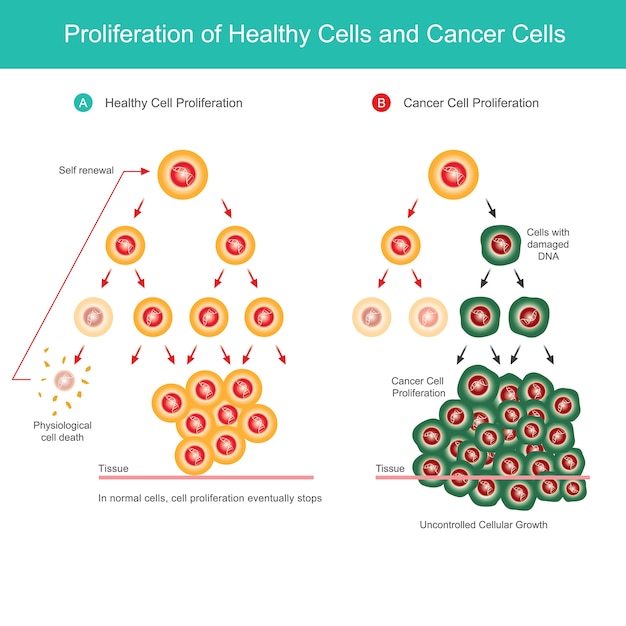
Tumors
A tumor, or neoplasm, is a mass of cells that break the healthy cell rules. Benign tumors are not cancerous and only break rule 1 (stop diving when connected to another cell or tissue). Benign tumors stay in the same place and cannot spread to other parts of the body. However, the term “benign” can be misleading. A benign tumor in a blood vessel can impede blood flow, or a lung tumor can reduce airflow. So, benign tumors are sometimes removed from the body so an organ can function properly.
Malignant tumors are cancerous, and they break all the healthy cell rules. The most dangerous rule that they break is their ability to spread to other tissues, called metastasis. Cancer’s ability to metastasize other tissues is what makes it deadly. For example, malignant melanoma is the deadliest form of skin cancer. If a mole becomes cancerous, a doctor can easily remove it via minor surgery. However, if a piece of the tumor (cancerous mole) breaks off and moves into the blood, it can travel to any part of the body. Therefore, a malignant tumor that originates in the skin can lead to tumors in the lungs, liver, kidneys, brain, or other organs. You can have a piece of your skin removed and live. But, you cannot live without your lungs.

Why is Cancer Deadly?
I had a college roommate that would eat my food when I was in class or at work. When I came home, I usually had nothing to eat, so I would have to go to the store. After a 16-hour day (8 hours in class and 8 hours working), all I wanted to do was sit on my couch and eat a turkey sandwich. Over a few weeks, the money I lost due to my roommate’s stealing wore me down, and I eventually stopped buying food for the apartment.
Did your roomate every pay you back?
No.
Why didn’t you evict him?
Well, evicting someone in San Francisco is a long and laborious task and the results are mixed.
So, how does your college roommate relate to cancer?
Well, cells that become cancerous steal oxygen and nutrients from healthy cells, and they no longer perform their jobs; hence, my roommate. Cancer eventually leads to organ failure when the nonfunction-nutrient-stealing cancerous cell population gets to a point where the remaining healthy cell can no longer do the work to keep the organ functioning.
How do cancer cells steal food?
Cancers can spawn their own blood supply, which diverts blood from healthy cells, starving them. Angiogenesis is the process of making blood vessels and cancer excells at this task.

What causes Cancer?
Most cancers occur spontaneously. However, lifestyle choices can increase or decrease the risk of getting cancer. Smoking and vaping (tobacco or marijuana) are carcinogens because they are chemicals that increase the likelihood of lung, mouth, and throat cancer (lung cancer is the most common type of terminal cancer.) Sun tanning, especially tanning salons, increases the risk of malignant melanoma. A diet high in saturated fat and sugar and/or a lack of daily exercise increases the cancer risk.
Viruses can also lead to cancer. For example, the human papillomavirus (HPV) is the leading cause of cervical cancer (the opening to the uterus) and vaginal cancer in women, penile cancer in men (cancer of the penis), and anal cancer in both men and women.
Cancer Treatments
Prevention is the best cancer treatment. A diet rich in unsaturated fat, lean protein, veggies, and whole grains, daily exercise, and abstaining from nicotine, drugs, and alcohol reduce the risk of a cancer diagnosis.
Cancer is usually treated via removal (surgery), radiation, or chemotherapy. Chemotherapy is a concoction of drugs that kills cells in cell division. Cancer cells spend most of their time dividing, so chemotherapy usually kills most types of cancer. However, the chemicals also kill healthy dividing cells, such as skin cells, hair follicle cells, and the cells lining the intestines.
There are new treatments using lasers, heat, and viruses as cancer treatments.