The Idea of Evolution Preceded Darwin
You may have read or heard that Charles Darwin was the first person to develop an evolutionary hypothesis. Well, that’s not correct. The ancient Greeks, Romans, Chinese, and medieval Islamic scientists had assumptions that life and the Earth’s geography changed with time. However, Aristotle’s hypothesis that life does not change with time became the dominant premise of science and religious dogma and would remain so for nearly two millennia.
Darwin was the first person to collect evidence and publish his hypothesis explaining natural selection. Natural selection is one of the most significant scientific discoveries because it explains how the primary mechanism behind evolution works. However, natural selection was not received well in western science because it challenged the science and religious convictions in 19th century Britain. Darwin did not live to see his hypothesis become a theory, but natural selection has been proven to be the main driving force behind evolution after years of experimentation.

What is a Common Ancestry?
You probably have seen the figure of evolution below.
What you may not know is that this figure is a false representation of evolution. Humans were never monkeys, chimpanzees, or Neanderthals, and monkeys, apes, and Neandertals were never humans.
So, there is no relation between humans and other animals?
No, we are related.
What?!!!
We are related because we share a common ancestor with monkeys, apes, and Neanderthals.
How is a common ancestor different than the figure above?
Well, about seven million years ago, a population of primates was living in Africa. The population separated, and over time, one population evolved into chimps and the other into modern humans. However, this was a gradual change, with many transitional species between modern humans and chimps and the common ancestor.

Therefore, calling chimps our brothers or sisters or parents is not correct.
Why?
Because chimps are our cousins.
What?????
Let me explain. Do you and your cousin share the same biological parents?
That’s a question, not an explanation.
Point taken. But, do you share the same biological parents with your cousin?
No.
Are you your cousin’s child or vice versa?
No.
Therefore, what is the common ancestor you and your cousin share?
Our grandparents?
Yep. Neither you nor your cousin came directly from your grandparents, but your grandparents are the common ancestor you and your cousin share. You are not your grandparent’s offspring, but without your grandparents, you would not exist. The same is true about the common ancestor humans and chimps share. Neither species directly evolved from our common ancestor, but without it, neither species would exist.
Evidence for Evolution
This chapter will focus on six types of evidence that support the theory of evolution.
Evidence #1: Geology
Knock Knock.
Who’s there?
Rocks
Rocks who?
Some rocks date back 4.2 billion years when the Earth’s crust cooled and became solid rock.
You are more than welcome to use that joke at your next social gathering.
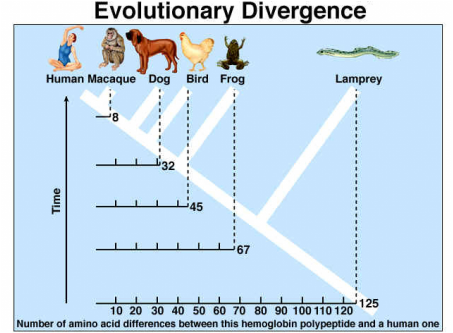
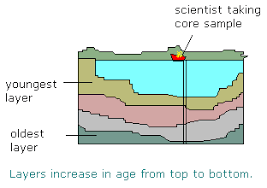
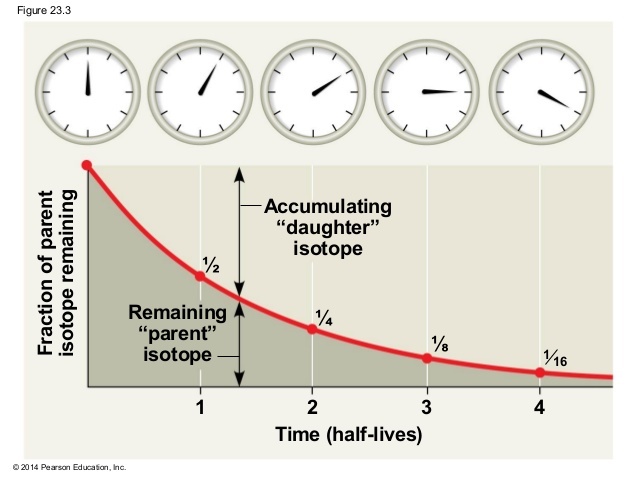
We can gauge the age of rock by using relative dating and radiometric dating. Relative dating compares rock layers, with the oldest rocks on the bottom and the newest on top. Radiometric dating measures the number of radioactive isotopes in a layer of rock. The more the isotopes that have decayed, the older the rock. These two methods of dating rock layers are important in determining the age of a fossil because it is the rock layer the fossil is in that is dated, not the fossil itself.
| This is Relative Dating | This is Radiometric Dating | This is the First Question Everyone Must Ask Themselves at the Start of Each Day |
|---|---|---|
 |  |  |
Evidence #2: Fossils
Fossilization is the process of making fossils. Fossilization is a rare event because it happens only within specific conditions. The first condition is a lack of oxygen. Oxygen is a very reactive element, and dead organisms decompose rapidly in its presence. Organisms covered in silt, sap, and volcanic ash are more likely to fossilize because these environments are usually anaerobic.
The second and third conditions are time and pressure. Fossilization is a slow process requiring an immense amount of pressure. Pressure helps replace organic matter with inorganic matter, which creates a “copy” of the organism in a fossilized form.
The fossil record shows us how organisms changed with time. For example, we have found transition fossils that show the evolution of whales from a four-legged terrestrial species to today’s legless aquatic giants.

Evidence #3: Homologous Structures
Homologous structures share a similar morphology (the body structure of an organism) but may have a different function. The forelimbs of bats, cats, whales, and humans all comprise the same bones. However, the bone arrangement varies due to the function of the forelimb. For example, whale, cat, bat, and human forelimbs contain a humerus (arm bone), radius and ulna (forearm bones), carpals (wrist bones), metacarpals (hand bones), and phalanges (finger bones). However, the bones are arranged differently, so a whale can use its forelimb for swimming, a bat for flying, a cat for walking, and a human from grasping.
So are bat wings and bee wings homologous structures?
No, they are analogous structures.
What the turtle?!!!!!
Analogous structures have the same function but have a different evolutionary origin. Bats and bees use their wings for flight, but they are made of different materials and evolved separately.
The major organs between mammals are homologous structures as well. My physiology students can dissect a cat to learn human anatomy because cats and humans have the same major internal organs and similar muscle groups. For example, the chest cavity in a human and a cat contains the heart and lungs, and the abdominal cavity contains the digestive organs and kidneys.


Organisms are not built from scratch but are the products of modifications that give each species its similar yet unique biology. For example, a giraffe’s neck is nearly half its body length, while a human’s neck is about 10 percent its body length. However, humans and giraffes have seven neck bones (cervical vertebrae). The difference between human and giraffe vertebrae is the size, not the number.

Here’s the Part of the Chapter Where Bees Explode

Evidence #4: Vestigial Structures
Vestigial structures are structures with no function in an organism but had a function in past ancestors. Arguably, the most famous human vestigial structure is the appendix. In herbivores, the appendix is a functional structure that digests fiber in plants to extract more energy from vegetation. Humans cannot digest fiber because their appendix has lost that function.
Why did our appendix lose its function?
Good question.
Thank you.
Over time, our ancestors gained the ability to extract energy from meat, which is easier to digest than fiber. So, the appendix became redundant and lost its function.
Why do we still have an appendix if it has no function?
Evolution selects traits based on their benefits or disadvantages. Species with beneficial traits are more likely to survive and reproduce, and organisms with harmful traits are less likely to survive and reproduce. However, traits that do not affect an organism’s survival are neither selected for or against. Therefore, a vestigial trait remains in a species long after it loses its function. For example, male nipples are vestigial structures. But male nipples do not increase or decrease the chances of survival – though, they do ruin the bat suit. However, in rare instances, a male can lactate (produce breast milk) and breastfeed their child.

Evidence #5: Embryo Homologies
The picture below shows the embryonic and fetal development of several vertebrates (organisms with backbones). What similarities are there between the species?

They all look the same in the top row. They have tails and eyes on the side of their heads.
Awesome possum!!! When do the organisms appear different from each other?
They begin to look different in the second and third rows.
Awesome possum, possum awesome!!!! The embryos (the first stage of development) of vertebrates have similar characteristics – i.e., gill slits, tail, eyes on the side of the head. Differentiation between the organisms does not become apparent until they reach fetal development (a later pregnancy stage). Since all vertebrate embryos have similar structures, this supports the fact that all vertebrates share a common ancestor.
Evidence #6: DNA and Amino Acid Sequences
Darwin married his first cousin, a common centuries-long practice among prominent families in most of Europe.
Why was this common practice?
Ask your history teacher.
Did they have children?
Yep, ten children, but three of them died before they reached adulthood. The death of his children impacted his studies on evolution.
How?
Arguably the biggest question Darwin could not answer is how organisms pass traits on to the offspring that give them their fitness (how well an organism can survive in their environment). Darwin had a hunch that heredity had something to do with natural selection but could not explain the inherited thing or things. He also wondered if reproducing with a relative was the cause of the death of his children. But, he never found an answer to his hunch.
How did he not know that reproducing with a cousin increases the chance of genetic mutations?
The study of genetics was in its infancy in the mid 19th century and no one knew what the heritable material was. Therefore, there is no way of knowing if Darwin’s marriage to his first cousin was the cause of his children’s death. There were no antibiotics and few vaccines during the 19th century, and the loss of a child was much more common than it is today. (Abraham Lincoln, who shares the same birth date as darwin, February 12, 1809, had four children, but only one survived into adulthood.) Darwin even included offspring mortality in his hypothesis on natural selection, explaining that organisms have many offspring, which increases the chance that some will survive long enough to reproduce and pass on their traits to the next generation.
So how does Darwin marrying his first cousin relate to evolution?
At the same time Darwin published his Theory of Natural Selection, Gregor Mendel was experimenting with the inheritance of pea plants’ traits. However, Darwin never read Mendel’s work, and scientists discovered the link between Darwin’s and Mendel’s work years after both scientists had died. Mendel’s work explained what Darwin could not: organisms inherit genes from their parents that code for traits that may or may not increase the organism’s fitness (survival and reproduction).
Our DNA shows our history through time and contains the remnants of our ancestors. All organisms use the same four DNA molecules – A, G, T, and C. What makes a human different from a bat is the arrangement of those four letters. For example, software code comprises of ones and zeros. Software developers use ones and zeros to code for The Legend of Zelda and Metroid. However, the order of the ones and zeros are different between the two programs. Therefore, one combination of ones and zeros produces Link and his adventures in Hyrule, and another combination directs Samus through her journey on Zebes.
Human DNA consists of DNA pieces from our animal ancestors and single-celled ancestors. For example, 2% of our DNA comprised genes but almost 10% contains viral DNA.
DNA is the cookbook of life that codes for amino acids, which are the building block of proteins. The DNA tells cells the sequence of the amino acids for each protein. Therefore, organisms that share a recent common ancestor will have similar DNA and similar amino acid sequences. Organisms that are distantly related will have more differences in their DNA and amino acid sequences.