The heart is the first functional organ to develop in utero. Eighteen days after fertilization, a single cell begins to beat. That cell multiplies into two cells, and those two cells divide and become four cells. The cell division is so rapid that it takes a mere three days for the heart to start pumping blood.
Blood
Blood comprises cells and a liquid called plasma. Fifty-five percent of the blood’s volume is plasma. Dissolved in the plasma are nutrients such as glucose and proteins such as antibodies and clotting factors (proteins that help you blood clot).
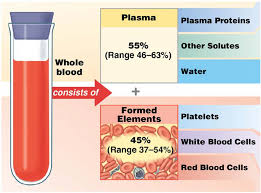
White blood cells (WBCs) are the cells of your immune system. WBCs’ primary job is to hunt and kill pathogens. Only two percent of your WBCs are in your blood. The other 98% are found in organs like lymph nodes and spleen.
Platelets are remnants of a cell that exploded (think Alderaan). Platelets help the tissues heal by forming blood clots.
| This is a Megakaryocyte Exploding into Platelets | This is the Death Star Destroying Alderaan |
|---|---|
 |  |
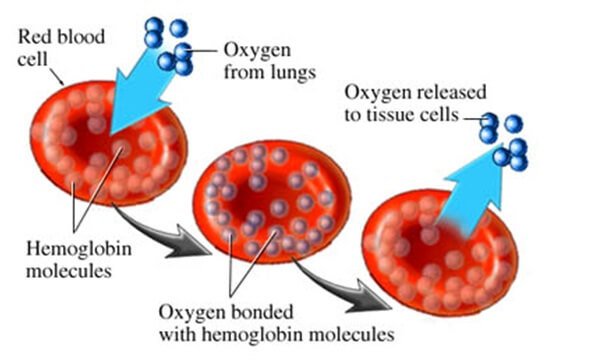
Red blood cells (RBCs) will be the focus of this chapter because they carry oxygen and carbon dioxide. RBCs contain the oxygen-carrying protein hemoglobin. When oxygen diffuses into an RBC, it binds to hemoglobin, which turns the RBC bright red. RBCs without oxygen deep red in color. Humans and all other vertebrates (except the ice fish) have red blood.
Wait, I thought deoxygenated blood is blue.
Even deoxygenated blood is still contains about 65% oxygen, so oxygen-light might be a better description. Since your blood always has oxygen in it, remains a shade of red.
So, then why do textbooks color oxygen poor blood blue?
Coloring the right side of the heart and most veins blue and the left side of the heart and most arteries red, better contrasts the difference between oxygen-rich blood (99%) and oxygen-poor blood (65%).
So, no blue blood?
If you have blue blood, then you are a king crab.
I’m not a crab.
Thanks for clarifying that.
Anyway, red blood cells look like donuts because of their concaved center(they do not have a hole in the center, though). The concaved shaped forms when they eject their nucleus during maturation. RBCs make ATP anaerobically and they do not have mitochondria. The lack of mitochondria prevents them from using the oxygen that they are carrying.
Blood Vessels
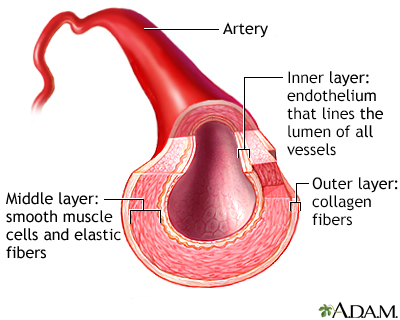
Blood vessels are the roadways of the body. You have about 100,000 miles of blood vessels in the body with a diameter range from that of a quarter to a single strand of hair. There are three primary types of blood vessels in your body. Arteries take blood away from the heart. Veins carry blood towards the heart. And the movement of water, gasses, nutrients and happen through the capillaries’ walls.
A common misunderstanding is that arteries are larger than veins. Arterial walls are twice as thick as the walls of veins; however, a vein’s lumen, the inner space containing the blood, is five times larger than arterial lumens. Capillaries have the smallest lumen and thinnest walls of the blood vessels.
Arteries
Arteries take blood away from the heart and move it towards the body’s tissues. The heart pumps blood into the arteries; therefore, the blood pressure is highest in the arteries. Arteries have thick, elastic muscular walls that can withstand dynamic pressure changes.

Capillaries
Capillaries are tubes formed from a single layer of cells. Capillaries have the smallest lumen, but they have the greatest surface area. The high surface area increases the diffusion rate through their thin walls, which ensures fast gas exchanged between the blood and body tissues, and the blood and the lungs happen.
Veins
Veins move blood towards the heart. Veins the largest lumens, but their walls are thinner than arteries. There is almost no blood pressure within the veins, so they do not have thick, muscular walls. Gravity primarily moves the blood in the veins superior to the heart. Veins that are inferior to the heart push the blood via skeletal muscle contractions.
The veins below the heart contain valves. When skeletal muscles contract, they squeeze the veins, which pumps the blood towards the heart. However, when the muscles relax, the force of gravity pulls the blood towards the feet. The one-way valves within the veins prevent the blood from pooling in the lower extremities.


Heart Structure
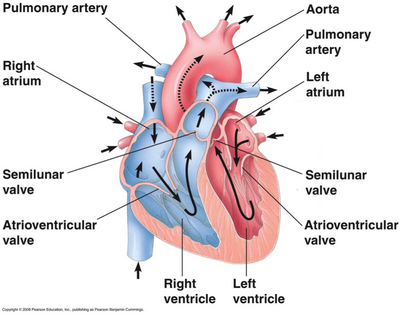
The heart has four chambers. The two upper chambers are the left and right atria, and they received blood from the veins. The two lower chambers are the left and right ventricles, and they pump blood into the arteries.
Between the atria and the ventricles are the AV valves. The AV valves keep the blood flowing in one direction. When the ventricles contract, the AV valves close, preventing blood from reentering the atria. The semilunar valves are between the ventricles and the arteries. When the ventricles relax, the semilunar valves close, preventing the blood in the arteries from re-entering the ventricles.

Inspiring and Expiring
Did you know that we inspire and expire an average of 15 times per minute?
Inspire who? And, we die 15 times a minute?!!!!!!!
No, inspire and expire refers to breathing. Inhaling is to inspire and exhaling is to expire.
Did you know chocolate dragons expire chocolate milk?

The Respiratory Tract
The respiratory tract is the pathway through which the air you breathe flows into the lungs. When we inhale, the diaphragm (a muscle below the lungs) contracts downwards, forcing air to move in through our nose and mouth.


The air moves then moves through the following structures:
- The larynx is the voice box because it contains the vocal cords.
- The trachea is the tube you can feel in the middle of your neck.
- The bronchial tubes carry the air into the lungs.
- The alveoli are at the end of the respiratory tract and this is where oxygen diffuses into the blood and carbon dioxide diffuses into the lungs.


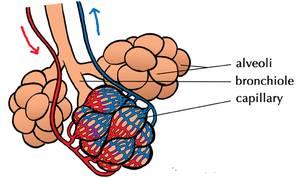
Gas Exchange
Gas exchange occurs between the alveoli and the capillaries that surround them like a spider web. The walls of the capillaries and alveoli are one cell thick which allows for the rapid diffusion of oxygen into the blood and the rapid diffusion of carbon dioxide out of the blood. Once in the blood, oxygen diffuses into RBCs and binds to hemoglobin. The oxygen-rich blood returns to the left side of the heart and the left ventricle pumps the blood to the body’s capillaries. At the capillaries, oxygen diffuses out of the RBCs and into the body cells and carbon dioxide diffuses out of the body cells and into the RBCs and binds to hemoglobin. The deoxygenated blood returns to the right side of the heart and the right ventricle pumps the blood to the capillaries that surround the alveoli.


AP Bio and Physiology Prep
Here is a link to the Physiology chapters on the heart and blood vessels and gas exchange.